The Mission:
Defuse Drug Resistant Infections
Drug-resistant infections are making routine surgeries, cancer treatments, and minor injuries dangerous again.
Marva Labs develops therapies that speak bacteria’s native language and signal them to self-destruct.
Redefining infection control as negotiation instead of warfare.
Marva Labs is pioneering cooperative biology: the foundation of post-antibiotic medicine.
The Problem:
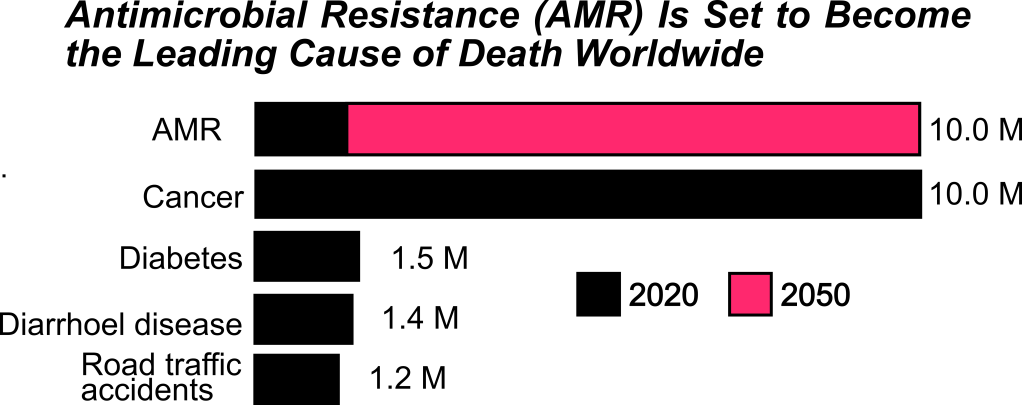
Antimicrobial resistance is a growing global health threat. In 2019, approximately 1.27 million deaths were directly attributed to AMR, with nearly 5 million deaths associated with drug-resistant infections worldwide. In the United States alone, over 2.8 million AMR infections occur annually, resulting in more than 35,000 deaths.

The economic burden of AMR is substantial and escalating. In the U.S., treating just six of the most concerning AMR threats contributes to over $4.6 billion in healthcare costs each year. Globally, if current trends continue, AMR could lead to additional healthcare costs of up to $159 billion annually by 2050.
The Solution:
At Marva Labs, we are pioneering a novel antimicrobial platform that exploits bacterial communication systems to induce self destruction. Our flagship product, EndoVox™ (derived from endo- meaning “within” and vox meaning “voice”), utilizes death-phase extracellular vesicles (D-EVs) to deliver native microbial signals that trigger ferroptosis—an iron-dependent oxidative death pathway. By disrupting redox balance, enhancing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and silencing quorum sensing, EndoVox™ effectively causes pathogens to dismantle themselves from within.
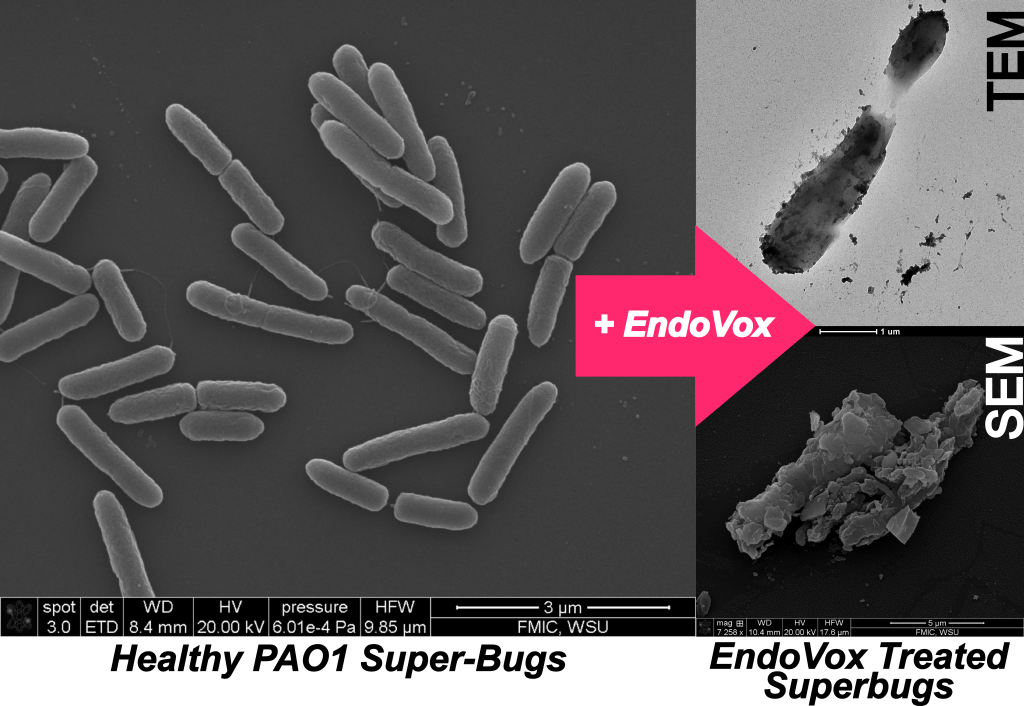
This mechanism has demonstrated potent efficacy against a broad spectrum of drug-resistant pathogens, including Gram-positive bacteria like MRSA, Gram-negative bacteria such as P. aeruginosa, and even resilient fungal biofilms like Candida auris. EndoVox™ offers a targeted, biocompatible approach to combating some of the most formidable superbugs in modern medicine.
Traction
- Patent pending: Composition, extraction method, and therapeutic use of D-EVs
- Raised $150K+ in non-dilutive funding from grants, pitch competitions, and commercialization awards
- I-Corps backed: Completed NIH/NSF I-Corps validating market and clinical need
- In vivo efficacy: >3.5-log bacterial reduction and >30% wound healing in murine model
- Clinically relevant safety: No cytotoxicity in human stem cells or LPS contamination detected

